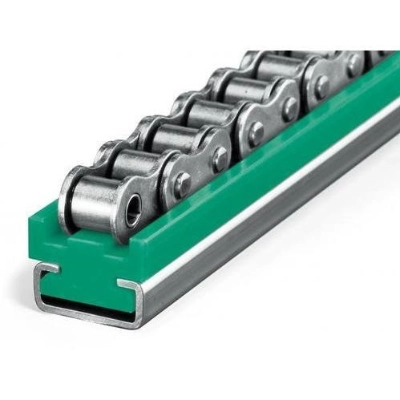
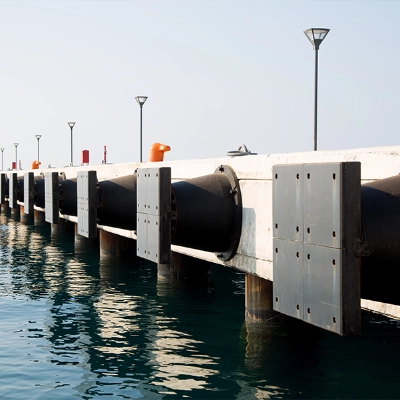
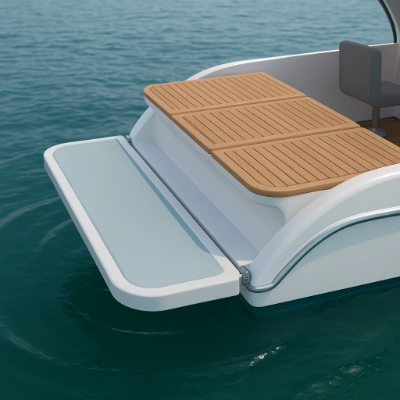
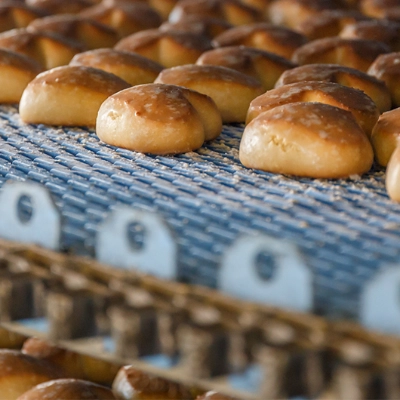
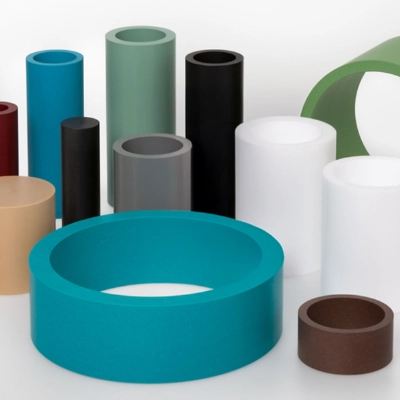
What is a Roller?
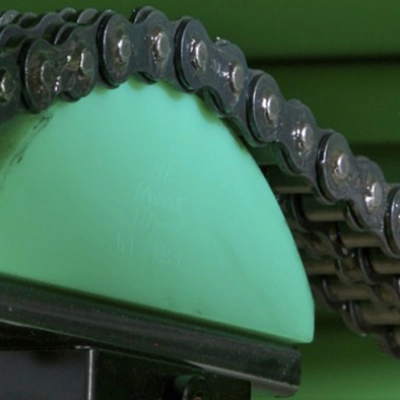
Generally plastic rollers are non-drive rollers, that is, idler rollers used to allow movement of equipment as part of a device, or to allow the smooth movement or transition of materials or products over the roller(s).
Benefits of Plastic Rollers vs Metal Rollers
- Noise Reduction – especially when operating on hard surfaces, plastic rollers will generate less noise.
- Smooth Operation – due to plastics have lower stiffness the roller will operate in a smoother manner generating less vibration.
- Light Weight – In addition to reducing the overall weight of a piece of equipment or system, light weight rollers, such as Ertalon 6PLA (1/7 the weight of steel) have less inertia and therefore rolling resistance.
- Reduced wear – plastic rollers generally will have better wear life, especially when operating on hard materials, such as metals or concrete.
- Cost-Effective – plastics are normally cheaper, but also provide further cost-benefits.
Benefits of Plastic Rollers vs Polyurethane Rollers
- Cost-Effective – plastic generally offers a commercial benefit over polyurethane.
- Chemical resistance – plastics offer broader chemical and solvent resistance.
- Eliminate Hub – often polyurethane rollers are cast onto steel hubs to be fitted to a shaft or have bearings inserted. These hubs can be eliminated with plastic rollers, i.e. they can be fitted directly to a shaft, or have bearings fitted directly, and retained by traditional techniques such as press-fits and/or cir-clips/retaining rings.
Dotmar has qualified engineers that can provide direct support with plastic rollers, by conducting load capacity calculations.