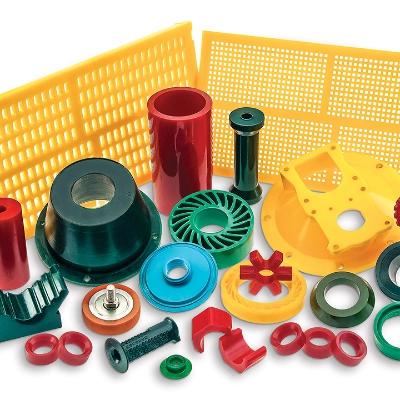
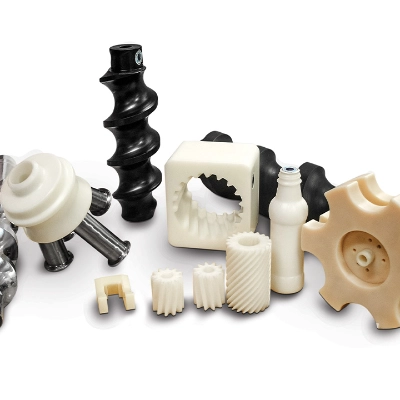
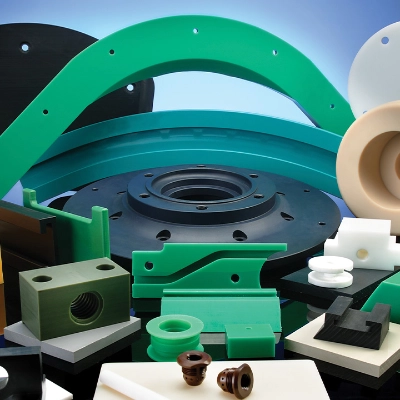
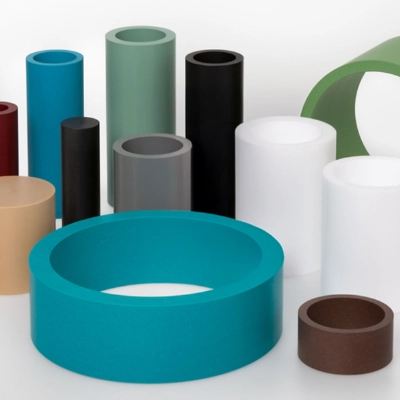
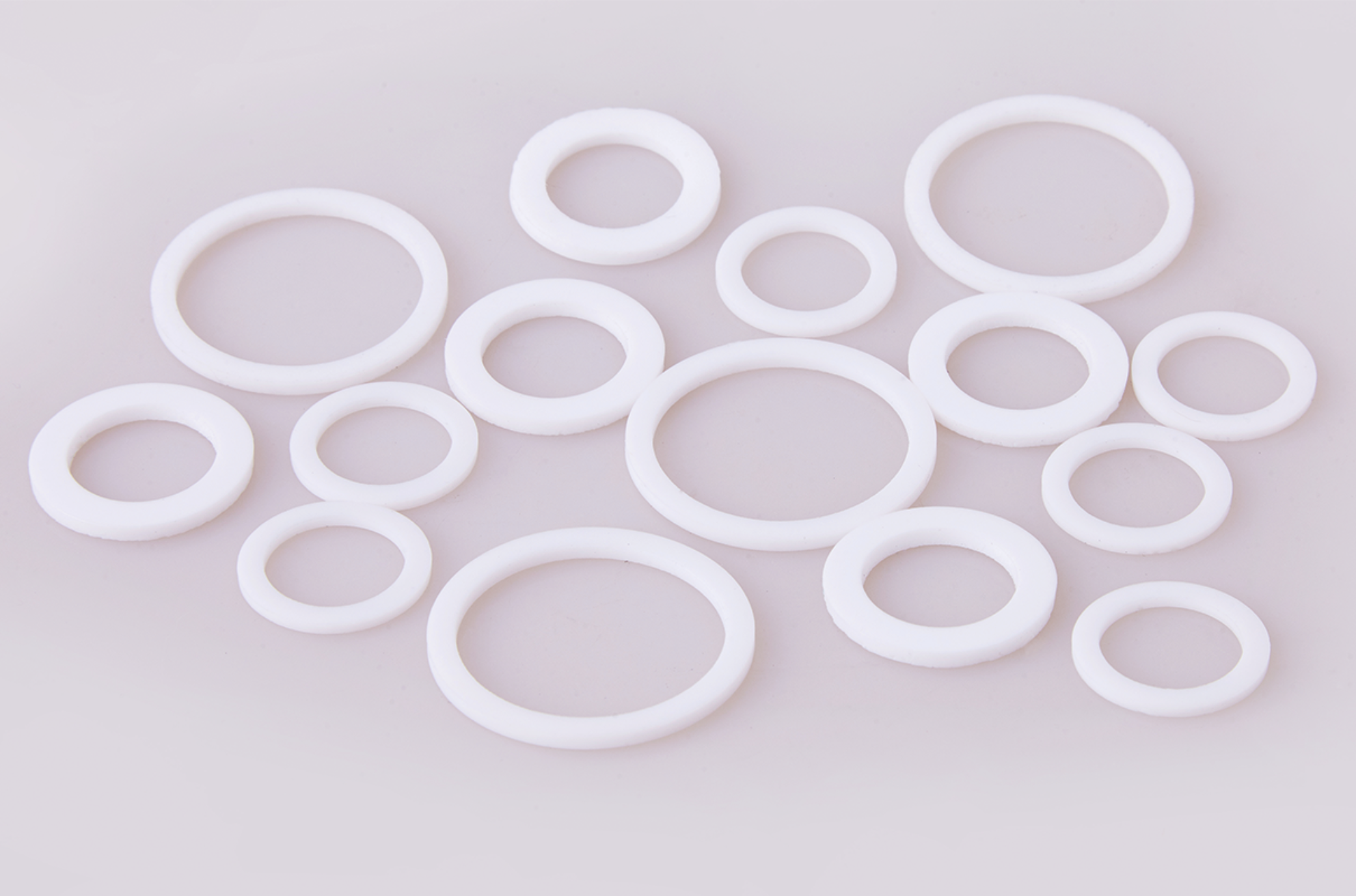
What is a Plastic Seal?
This is generally referring to a device that is used to retain lubricants (such as oil or grease) within a system and prevent contaminants (such as dust, dirt or liquids) from entering. They can be either static or dynamics seals.
Benefits of Plastic Seals vs Other Materials
- Low Friction – For dynamic seals running on a hard surface, such as steel, plastics such as Tetron S, Polystone 7000, Ertacetal C and Ertalon LFX, tend to have low friction compared to rubbers and polyurethanes, which results in lower drive forces (and energy consumption) and heat generation.
- High Speed – due to the low friction and heat generation, plastics can tend to tolerate higher surface speeds.
- Corrosion Resistance – Plastic seals are often resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other corrosive substances is a concern.
- Reduced wear – Plastics have very good wear and abrasion resistance, resulting in improved service life.
- Cost-Effectiveness – machined plastics seals don’t require the up-front cost of tooling, therefore are cost effective for short production runs.
Dotmar has qualified engineers that can provide direct support with plastic seal material selection to suit the application needs.